1. Fossil:
Are the remains, imprints, or traces of prehistric organisms.2. Permineralized remains:
Are fossils in which the spaces inside are filled with minerals from groundwater.
When a thin film of carbon residue is left, forming silhouette of the original organism.
4. Mold:
A type of fossil that forms in rock when a organism with hard part, decays or dissolves, and leaves, and leaves a cavity in rock.
5. Cast:
A type of body fossil that forms when crystals fill a mold or semiments wash into a mold and harden into rock.
6. Index Fossils:
Are the remains of species that exist on Earth to relatively short periods of time, were abundant, and were widespread geographically.
7. Principle of Superposition:
States that in undisturbed rocks layers, the oldest rocks are on the bottom and the rocks become progressively younger toward the top.It is age in comparison to other things.
9. Unconformity:
10. Absolute Age:
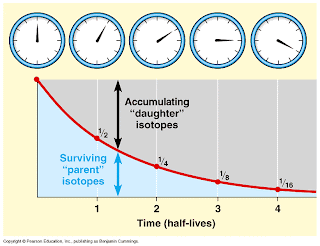
Is the age, in years, of a rock or other object.12. Half-life:
13. Radiometric Dating:
Process used to calculate the absolute age of rock by measuring the ratio of parent isotope to daughter product in a mineral and knowing the half-life of the parent.